shoulder tests rotator cuff tear orthopedic|rotator cuff tendon test : fabrication Shoulder Exam. Biceps tendinopathy refers to inflammation or degeneration of the long head of the biceps tendon. It is an important cause of anterior shoulder pain and it is usually seen in association with other shoulder pathologies, such . Resultado da 294K Followers, 857 Following, 24 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Mari Ávila 🐝 (@mariavila)
{plog:ftitle_list}
4 dias atrás · Vídeo que circula nas redes sociais mostra minutos antes de Wanderson Costa Pacheco, 22, ser morto a tiros por dois homens em Juruena (880 km ao Noroeste de Cuiabá). Os suspeitos, que já foram presos, são integrantes do Comando Vermelho atuante no Noroeste de Mato Grosso e durante o crime, pedem à vítima ‘pedir desculpa .
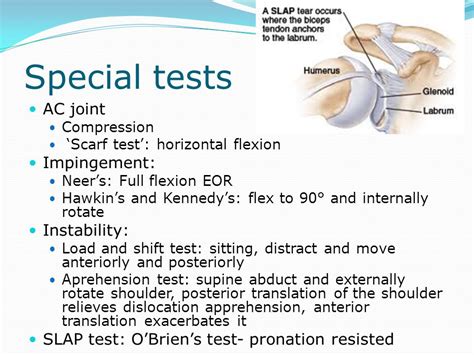
Traditionally Orthopaedic Special tests were used to assist in the diagnostic process by implicating specific tissue structures that are either dysfunctional, pathological, or lack structural integrity, confirming the findings from the physical assessment and providing a tentative diagnosis. Special testing . See more
However, although Orthopaedic Special Tests are commonly used, findings from both narrative, systematic reviews, and research investigations have consistently questioned the value of these procedures as a method of implicating the structures associated with . See moreOrthopaedic Special Tests may help us with symptom reproduction which can be used to test and retest following therapeutic interventions to assess for any change in symptoms. . See more
Shoulder Exam. Biceps tendinopathy refers to inflammation or degeneration of the long head of the biceps tendon. It is an important cause of anterior shoulder pain and it is usually seen in association with other shoulder pathologies, such . technique. passively flex the elbow to 90 degrees, holding wrist to rotate the shoulder to maximal external rotation. Tell the patient to hold the arm in that externally rotated .
Rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young . Rotator cuff tears are common injuries caused by damage to the muscles or tendons that stabilize your shoulder joint. They can be diagnosed by using a number of tests and imaging techniques During the physical exam, health care providers will press on different parts of the affected shoulder and move your arm into different positions. They'll also test the strength of .If you have injured your shoulder or have chronic shoulder and arm pain, it is best to see an orthopaedic surgeon. They can then make a diagnosis and begin treatment. Your doctor may recommend a diagnostic imaging study such as a .
The first imaging tests performed are usually X-rays. Because X-rays do not show the soft tissues of your shoulder like the rotator cuff, plain X-rays of a shoulder with rotator cuff pain are usually normal and may show a small bone .
The major anatomical landmarks of the shoulder include the clavicle, the acromion, the acromioclavicular joint, the humerus, the subacromial space, the rotator cuff (including the. Move. The shoulder joint of each arm should be assessed and compared.. If the patient is known to have an issue with a particular shoulder, you should assess the ‘normal’ shoulder first for comparison.. Active .The rotator cuff tendons attach to the top of the humerus (humeral head) and connect the humerus to the shoulder blade's socket to allow you to move your shoulder and arm. There is a lubricating sac called a bursa between the .
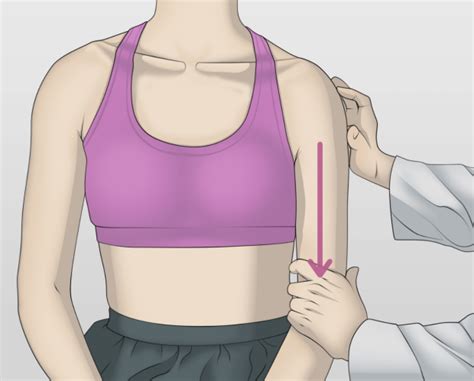
A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient slowly lowers the arm to .
The diagnostic value of the combination of patient characteristics, history, and clinical shoulder tests for the diagnosis of rotator cuff tear. Journal of orthopaedic surgery and research 2014;9(70) doi: 10.1186/s13018-014-0070-y.(1C) ↑ Smith MA, Smith WT.Rotator cuff tears: an overview. Orthopaedic Nursing. 2010;29(5):319-324.Arthroscopy Joint Replacement Preparing for Surgery Nonsurgical Treatments Diagnostic Tests Ortho-pinion Blog. View All Topics. . Rotator Cuff and Shoulder Rehabilitation Exercises. . After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. .The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as:Rotator cuff tears are more common in the dominant arm — the arm you prefer to use for most tasks. If you have a degenerative tear in one shoulder, there is a greater likelihood of a rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder — even if you have no pain in that shoulder. Several factors contribute to degenerative, or chronic, rotator cuff tears.
A New Orthopedic Test for Rotator Cuff Tears. Last month, the Journal of Shoulder & Elbow Surgery detailed a new rotator cuff orthopedic test that showed promising results for identifying rotator cuff pathology. In a study of 100 patients with MRI-defined rotator cuff tears, the Internal Rotation and Shift-Test (IRO/Shift-Test) demonstrated 92% sensitivity .Infrapinatus muscle is often involved in shoulder pathologies as shoulder impingement and rotator cuff tears. . may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and . Special Exam Maneuvers for Rotator Cuff Tear Empty Can Test/Jobe’s test. This test is positive if the examiner elicits weakness, which suggests a full-thickness tear– or pain, which suggests tendonitis. The patient abducts their arms, a little bit forward (at 10 and 2 o’clock). Have the patient push upward while the examiner pushes down. Dr.
air conditioner test seals
Rotator cuff tears are painful but most don't require surgery. Learn the symptoms of a torn rotator cuff, the road to recovery, and when surgery may be needed. . It is the most common upper extremity condition seen by primary and sports medicine doctors and orthopedic surgeons. Only rarely does a tear occur in the muscle itself. However, a .The rotator cuff is made up of four small muscles and their tendons that cover the head of your upper arm bone and keep it in the shoulder socket. Your rotator cuff helps provide shoulder motion and stability. Learn more: Biceps Tendinitis, Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis. Tendon Tears. Splitting and tearing of tendons may result from:Popping or crackling sensation that accompanies shoulder movement; Diagnosing Rotator Cuff Tears. To diagnose a rotator cuff injury or a possible rotator cuff tear, a Penn orthopaedic specialist will evaluate your symptoms, take a full medical history. and examine your shoulder and arm to assess your range of motion and how much pain you have. The O’Brien test can help diagnose a tear in the top or superior part of your labrum. A superior labrum tear is also called a SLAP tear, which stands for superior labrum, anterior to posterior. The O’Brien test can also rule out other problems, such as: Rotator cuff tear. Shoulder impingement syndrome.
Common Shoulder Tests in Orthopedic Examination. The following is a list of the many common tests used by physical therapists and other orthopedic practitioners when examining the shoulder. Some of the tests have links to .The prerequisite for any treatment in the shoulder region of a patient with pain is a precise and comprehensive picture of the signs and symptoms as they occur during the assessment and as they existed until then. Because of its many . As a rotator cuff tear becomes larger, retracted, and more degenerative in nature, the patient’s shoulder dysfunction will become more apparent as it becomes difficult for the rotator cuff as a group to function well. .
After a shoulder injury or surgery, . Arthroscopy Joint Replacement Preparing for Surgery Nonsurgical Treatments Diagnostic Tests Ortho-pinion Blog. View All Topics. By Body Part. . Rotator Cuff and Shoulder Rehabilitation Exercises . handout. After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily . A rotator cuff tear is a tear in the group of four tendons and muscles surrounding the shoulder joint. Learn about symptoms and how it is treated surgically or conservatively. . They may also have you complete additional tests to rule out other causes of shoulder pain. For example, if your pain extends down your shoulder and beyond your elbow .Rotator cuff tears are among the most common shoulder injuries. They happen when a rotator cuff tendon is separated, either partially or completely, from the bone. As you age, the risk of rotator cuff tears increases. That’s because rotator cuff tendons have a tendency to fray over time, making them even more vulnerable to damage.
Rotator cuff injuries that can cause shoulder pain include tendinitis, tears, and tendinosis. . Doctors use a variety of tests to diagnose rotator cuff problems. Imaging tests, such as an MRI, are especially important for figuring out the specific cause of your pain. . American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Rotator cuff tears. Factor D, .Symptoms Types of Rotator Cuff Tears. When the rotator cuff does not function normally, due to weakness, fraying or tearing, it may not function correctly to keep the humeral head (or "ball" at the top of the arm bone or humerus) centered on the glenoid (or "socket" attached to the shoulder blade). This causes abnormal motion at the joint and can result in "impingement" of . The rotator cuff can also be injured in a single incident during falls or accidents. Risk factors. The following factors may increase the risk of having a rotator cuff injury: Age. The risk of a rotator cuff injury increases with age. Rotator cuff tears are most common in people older than 60. Some occupations.Purpose [edit | edit source]. To test the presence of a shoulder full-thickness rotator cuff tear using the Drop-Arm Sign, Painful Arc Sign, and the Infraspinatus Muscle Test.. Evidence [edit | edit source]. Based on the Park et al study, the combination of the following 3 special tests have produced the highest post-test probability to diagnose a full-thickness rotator cuff tear:
A rotator cuff tear causes shoulder pain and makes arm movements difficult. Your risk of a tear increases with age. . Your healthcare provider will perform a physical exam to check for shoulder tenderness, range of motion and . ORTHO Orthopaedic Surgery; About Bullet Health; . Shoulder Exam Shoulder Imaging . Rotator cuff arthropathy is a specific pattern of shoulder degenerative joint disease that results from a rotator cuff tear leading to abnormal glenohumeral wear and subsequent superior migration of the humeral head.The shoulder exam can be challenging in patients and confidence in your special tests skills can help improve diagnostic accuracy. . Rotator Cuff Disease: Infraspinatus/ Teres Minor. Hornblower’s Sign. [7] Itoi, Eiji. “Rotator cuff tear: physical examination and conservative treatment.” Journal of Orthopaedic Science 18.2 (2013): 197 .
stanford 25 shoulder exam
Como Funciona: Seleccione um cavalo de cada uma das seis corridas seleccionadas. . A funcionalidade do Desafio de 6 Cavalos encontra-se disponível à discrição da bet365 e a bet365 não garante a sua disponibilidade. A bet365 não poderá ser responsabilizada se a funcionalidade do Desafio de 6 Cavalos não se encontrar disponível por .
shoulder tests rotator cuff tear orthopedic|rotator cuff tendon test